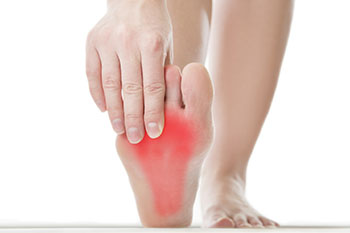
Plantar fasciitis affects the plantar regions of the foot, namely the heel, arch, and midfoot. When too much stress is put on the plantar fascia, or the connective tissue that stretches from the heel to the ball of your foot, inflammation, overtightening, and tearing may arise. This can cause foot pain. Because of plantar fasciitis, you may experience tearing with the first steps you take in the morning each day.
A certain trigger that may cause stress to the plantar fascia includes poor arch support, which is brought upon by frequently walking barefoot or wearing shoes with improper arch support. Other causes include obesity or a sudden increase in weight, increased physical activity, weak foot and ankle muscles, tight calf muscles, and arthritis.
If you’re feeling pain after sitting, walking, or standing for a long period of time, as well as when you first step out of bed or climb stairs, you may be showing signs of plantar fasciitis. To know for sure what’s causing you pain, it’s best that you get an x-ray taken of your foot.
Because plantar fasciitis is known to worsen over time, it’s recommended that you meet with Dr. Robert Leisten and Dr. Amy Haase as soon as possible for a proper diagnosis and advised treatment plan.
